Axilla - Anatomy of the Breast and Axilla
Location/Anatomic Boundaries
The axilla is a pyramidal space between the arm and the thoracic wall. It contains the axillary vessels and their branches, the brachial plexus and its branches and lymph nodes embedded in fatty tissue. Table 1.2 lists the boundaries and composition of the axilla. In addition, the apex is directed medially and upward and ends in the cervicoaxillary canal leading into the posterior triangle of the neck. The base is formed by axillary fascia and skin.
Fascia
The axillary fascia is an investing layer that extends from the pectoralis major to the latissimus dorsi muscles and encloses the hollow of the armpit.
It is continuous with the fascia covering the muscles that make the boundaries of the axilla. The clavipectoral fascia is a deep layer that extends from the clavicle to the axillary fascia in the floor of the axilla. It is separated into two sheets, in front and behind the subclavius muscle. At the lower portion of this muscle, it forms a single layer which extends laterally to the border of the pectoralis minor muscle. Here again it splits to surround the muscle.
The upper portion of the clavipectoral fascia, the costocoracoid membrane, lies between the pectoralis minor and subclavius muscles. It is pierced by the cephalic vein, the lateral pectoral nerve and branches of the thoracoacromial trunk. The lower portion of the clavipectoral fascia, located below the pectoralis minor muscle, is often referred to as the suspensory ligament of the axilla, or the coracoaxillary fascia. Here it is continuous with the axillary fascia.
Halsted’s ligament is a dense condensation of the clavipectoral fascia. It extends from the medial end of the clavicle to the first rib. The ligament covers the subclavian artery and vein as they cross the first rib. The axillary sheath is found at the apex of the axilla and forms a tubular sheath for vessels and nerves entering the axilla. It is adherent to the clavipectoral fascia under the subclavius and pectoralis minor muscles.
Axillary Artery
The axillary artery may be divided into three parts in the axilla based on its location in relation to the pectoralis minor. Table 1.3 lists the segments of the axillary artery.
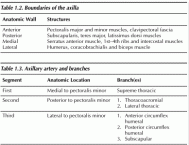 Table 1.2. Boundaries of the axilla
Table 1.2. Boundaries of the axilla