How to predict biphasic allergic reactions in children
Children are more likely to have a repeat, delayed anaphylactic reaction from the same allergic cause, depending on the severity of the initial reaction. The first pediatric study to look at the predictors for this phenomenon was published today in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.
Anaphylaxis is a severe, allergic reaction that is rapid in onset and can result in death. Some children are at risk of delayed (‘biphasic’) anaphylactic reactions. Delayed reactions occur when the initial symptoms of allergic reaction go away but then return hours or days later without exposure to the initial substance that caused the reaction.
A study led at the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario (CHEO) Research Institute looked at the frequency and severity of biphasic allergic reactions. From a sample size of 484 patient records, the incidence of biphasic reaction occurred in 15 percent of the study population, and two thirds occurred within six hours from the onset of the initial reaction. At least half of the biphasic reactions were serious in nature, and required treatment with epinephrine.
The study unveiled that biphasic reactions were more likely to happen if the initial allergic reaction was severe or if it was not treated with epinephrine. Furthermore, the anaphylaxis tended to be more severe when the administration of epinephrine was delayed.
‘The key message here for patients, parents, caregivers, teachers, and first-responder health professionals is: to prevent an anaphylactic reaction from worsening, administer epinephrine immediately after the onset of the early symptoms of an allergic reaction,’ said Dr. Waleed Alqurashi, emergency medicine physician at CHEO, and assistant professor at the University of Ottawa. ‘Our team has created an evidence-based prognostic tool so that physicians can monitor the more serious cases appropriately.’
The team identified five independent, evidence-based predictors of biphasic reactions in children, including:
Delay in presentation to the Emergency Department (or delay in epinephrine administration) of more than 90-minutes from the onset of the initial allergic reaction
Wide pulse pressure at triage
Treatment of the initial allergic reaction with more than one dose of epinephrine
Respiratory distress that requires administration of inhaled salbutamol in the Emergency Department
Children between the ages of 6 to 9 years old
 ‘It’s clear that children with severe initial reactions would benefit from a prolonged period of observation in the Emergency Department,’ continued Alqurashi. ‘On the flip side, knowing what to look for helps to better utilize resources so that children with mild allergic reaction, who do not match any of the identified predictors can go home faster.’
‘It’s clear that children with severe initial reactions would benefit from a prolonged period of observation in the Emergency Department,’ continued Alqurashi. ‘On the flip side, knowing what to look for helps to better utilize resources so that children with mild allergic reaction, who do not match any of the identified predictors can go home faster.’
The study entitled, ‘Epidemiology and clinical predictors of biphasic reactions in children with anaphylaxis’ includes clinical investigators and epidemiologists from the CHEO Research Institute, the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, University of Ottawa, and Memorial University.
Anaphylaxis Overview
Anaphylaxis (an-a-fi-LAK-sis) is a serious, life-threatening allergic reaction. The most common anaphylactic reactions are to foods, insect stings, medications and latex.
If you are allergic to a substance, your immune system overreacts to this allergen by releasing chemicals that cause allergy symptoms. Typically, these bothersome symptoms occur in one location of the body. However, some people are susceptible to a much more serious anaphylactic reaction. This reaction typically affects more than one part of the body at the same time.
Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical treatment, including an injection of epinephrine and a trip to a hospital emergency room. If it isn’t treated properly, anaphylaxis can be fatal.
Certain people are more at risk of anaphylaxis. If you have allergies or asthma and have a family history of anaphylaxis, your risk is higher. And, if you’ve experienced anaphylaxis your risk of having another anaphylactic reaction is increased.
Accurate diagnosis and successful management of allergies is essential. An allergist / immunologist, often referred to as an allergist, has specialized training and experience to diagnose the problem and help you develop a plan to protect you in the future.
Researchers reviewed health records of patients who presented to the Emergency Department with anaphylaxis at CHEO and the Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) based on the established diagnostic criteria of the National Institute of Allergy and infectious Diseases and the Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network.
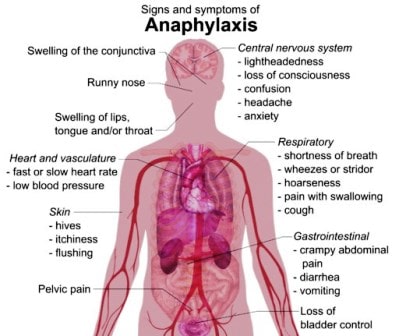
Anaphylaxis Signs and symptoms
Anaphylaxis most commonly affects the cutaneous, respiratory, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal systems. The skin or mucous membranes are almost always involved. A majority of adult patients have some combination of urticaria, erythema, pruritus, or angioedema. However, for poorly understood reasons, children may present more commonly with respiratory symptoms followed by cutaneous symptoms.[5]
Initially, patients often describe a sense of impending doom, accompanied by pruritus and flushing. Other symptoms can evolve rapidly, such as the following:
Dermatologic/ocular: Flushing, urticaria, angioedema, cutaneous and/or conjunctival injection or pruritus, warmth, and swelling
Respiratory: Nasal congestion, coryza, rhinorrhea, sneezing, throat tightness, wheezing, shortness of breath, cough, hoarseness, dyspnea
Cardiovascular: Dizziness, weakness, syncope, chest pain, palpitations
Gastrointestinal: Dysphagia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, cramps
Neurologic: Headache, dizziness, blurred vision, and seizure (very rare and often associated with hypotension)
Other: Metallic taste, feeling of impending doom
###
About the CHEO Research Institute
The CHEO Research Institute coordinates the research activities of the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario (CHEO) and is affiliated with the University of Ottawa. Its three programs of research include molecular biomedicine, health information technology, and evidence to practice research. Key themes include cancer, diabetes, obesity, mental health, emergency medicine, musculoskeletal health, electronic health information and privacy, and genetics of rare disease. The CHEO Research Institute makes discoveries today for healthier kids tomorrow.
About the University of Ottawa
The University of Ottawa is home to over 50,000 students, faculty and staff, who live, work and study in both French and English. Our campus is a crossroads of cultures and ideas, where bold minds come together to inspire game-changing ideas. We are one of Canada’s top 10 research universities - our professors and researchers explore new approaches to today’s challenges. One of a handful of Canadian universities ranked among the top 200 in the world, we attract exceptional thinkers and welcome diverse perspectives from across the globe.
###