|
Chilli peppers could help scientists to develop an effective treatment for patients with arthritis. Researchers in the United States have found a link between the pain associated with eating the peppers and the pain associated with arthritis.
The peppers and arthritis trigger the same chemical signals in the body that can cause pain.
The scientists said the discovery enhances their understanding of arthritis and could lead to new treatments in the future.
Dr Clifford Woolf and Dr Ru-Rong Ji of Massachusetts General Hospital found that proteins in the mouth react to the active ingredient of chilli peppers - capsaicin, which causes the "hotness".
The same protein is also activated with arthritic inflammation.
Pain triggers
The protein called TRPV1 sends chemical signals to cells triggering pain.
The performance of this protein is regulated by a single molecule. When this molecule is activated it can boost TRPV1 levels by up to 20 times.
The scientists said that blocking this molecule, called p38, could stop people with arthritis from suffering pain.
|
"We're starting to understand why patients with arthritis or other inflammatory conditions are likely to have increased pain and sensitivity to heat " |
|
Dr Clifford Woolf |
"We could use an inhibitor to p38 to block the increase in TRPV1, therefore blocking pain in patients who suffer from many diseases and conditions that involve inflammation," Dr Woolf said.
He added that the findings improved understanding of arthritis.
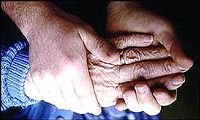
"With these findings, we're starting to understand why patients with arthritis or other inflammatory conditions are likely to have increased pain and sensitivity to heat," he said.
The study is published in the journal Neuron.
[ Nando Times ]
««« »»»
Last Revised at December 10, 2007 by Lusine Kazoyan, M.D.
|